My Garage
My Account
Cart
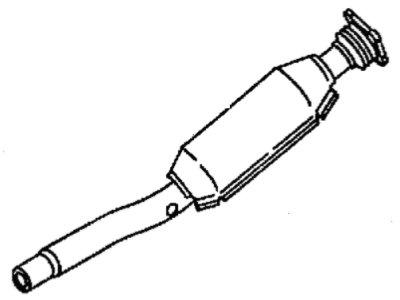
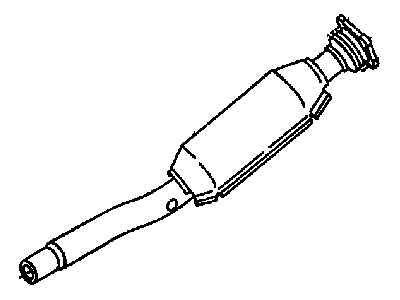
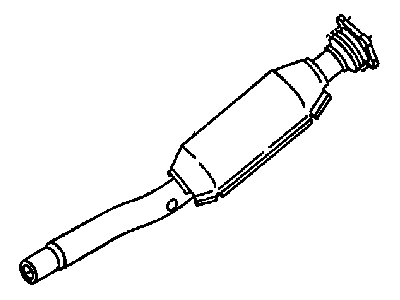
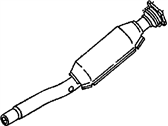
Genuine Chrysler Cirrus Catalytic Converter
Cat. Converter- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
7 Catalytic Converters found
Chrysler Cirrus Catalytic Converter
The Chrysler Cirrus has a catalytic converter as one of the major parts of the vehicle exhaust and emission manufacturer systems. The main purpose of this device is to reduce the formation of dangerous gases which are generated during the combustion process like the Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrocarbons (HC), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) into harmless products like water and Carbon Dioxide (CO2). Chrysler Cirrus made use of the catalytic converter that is composed with a honeycomb substrate embedded with the catalysts including platinum, palladium and rhodium to causing these chemical reactions. For the years the Chrysler Cirrus has used various styles of the catalytic converters, both direct and universal styles exist. Direct fit converters are much simpler to install as they are made specifically to fit particular automobiles while universal ones, need adjustments to be done in order to fit automobiles. Performance catalytic converters are also obtainable, for high flow to boost the performance of an engine as possible while ensuring the required efficiency of the catalysts. In all, the Chrysler cirrus catalytic converter is an important component given its role in minimizing emission and conforming to environmental accord.
Looking for affordable and high-quality auto parts? Then you have already arrived at the proper online shop. We offer all Chrysler Cirrus Catalytic Converter at great affordable prices. Moreover, all genuine Chrysler Cirrus Catalytic Converter come with a manufacturer's warranty. In the long run, you would realize you have saved a lot of trouble and money with OEM parts from here.
Chrysler Cirrus Catalytic Converter Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What Are the Inspection Procedures, and Repair Steps for the Catalytic converter and Muffler on Chrysler Cirrus?A:The exhaust works include the exhaust manifold, catalytic convertor, resonator, exhaust pipe, muffler and all associated brackets, hangers and clamps which attach to the body by means of supports and rubber hangers; any damage or improper fixing of these works may result in excessive noise and vibrations. Safety and noise level check should be conducted more frequently, with concern for damaged or bent parts, opened seams, holes, loose connections, excessive corrosion or deterioration, and flaws that permits exhaust fumes to infiltrate the vehicle, and damaged components should be replaced not fixed. It is suggested that application of penetrant oil to the fasteners prior to dismantling can help in freeing the nuts involved and for steering components that are severely rusted welding tools would be required; but in the absence of welders, one may resort to hacksaw to cut off the affected parts or pneumatic chisels; safety glasses/ gloves when wielding these tools should be worn. That is when repairing the exhaust system, one should progress from the rear end to the front, apply penetrating oil on the fasten, replace all gaskets hangers, and clamps, apply anti-seize compound on the thread of the fasteners while replacing them, and make sure that the new parts are not rubbing on under-body causing overheating. Besides, the heat shield should be visually inspected for cracks, dents and missing or loose fasteners from time to time, and in the event the catalytic converter has gone bad, detaching the exhaust system from the catalytic converter, attaching a replacement using new gaskets and tightening new fasteners is the way to go.