My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Dodge Challenger Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
18 Fuses found

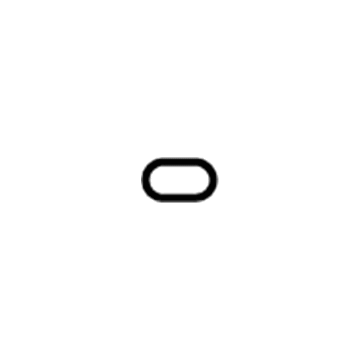
Dodge Challenger Fuse-Mini Low Profile
Part Number: 68137033AA$2.33 MSRP: $3.45You Save: $1.12 (33%)


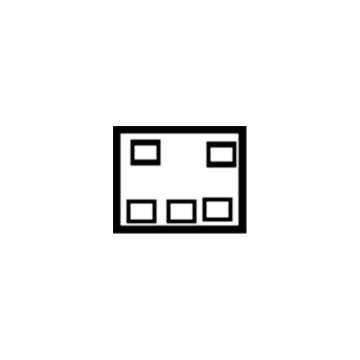
Dodge Challenger Fuse-Mini Low Profile
Part Number: 68137024AA$2.33 MSRP: $3.45You Save: $1.12 (33%)
Dodge Challenger Fuse-Mini Low Profile
Part Number: 68137031AA$2.33 MSRP: $3.45You Save: $1.12 (33%)


Dodge Challenger Fuse-Mini Low Profile
Part Number: 68137035AA$2.33 MSRP: $3.45You Save: $1.12 (33%)

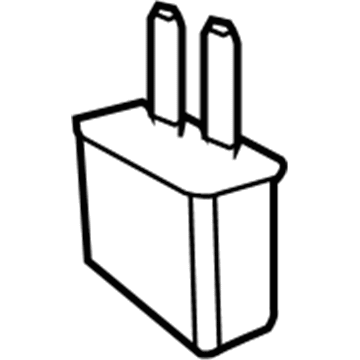
Dodge Challenger Fuse-Mini Low Profile
Part Number: 68299945AA$4.91 MSRP: $6.50You Save: $1.59 (25%)
Dodge Challenger Fuse
Looking for affordable and high-quality auto parts? Then you have already arrived at the proper online shop. We offer all Dodge Challenger Fuse at great affordable prices. Moreover, all genuine Dodge Challenger Fuse come with a manufacturer's warranty. In the long run, you would realize you have saved a lot of trouble and money with OEM parts from here.
Dodge Challenger Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How are the electrical circuits of safeguarded, and what should be considered when replacing fuses and fusible links on Dodge Challenger?A:The wiring circuits of the vehicle are protected by means of fuses and Relays; the engine compartment fuse and relay unit is mounted on the right front corner of the engine compartment while the rear fuse and relay unit is located in the trunk behind the spare tire access cover. To get to either of the boxes, one has to flip open the lid. Some manufacturers for example use the terms Integrated Power Module or Power Distribution Center to mean the fuse & relay boxes & it is useful to have these factory terms when buying fuses or relays. There is a tag specifying which circuit it inspires on the fuse panel, and these are available in standard and 'mini' and 'maxi' sizes, additionally, most fuses should be removed by using electronics needlenose pliers or a small fuse-puller tool which is usually housed in the fuse and relay box. If an electrical component resists and an electrical check is done and the fuse is observed to be missing, using a test light to verify power at the terminal tips; if power is present on one side of the fuse but does not get to the other side of the fuse then the fuse is bad and can be easily noticed. If the fuses are blown they must be replaced with fuses of the right type as different fuses cause problems; the amperage rating is printed on the fuse body. In case a new fuse is replaced and blows immediately, the cause of the problem should be looked at and fixed, say because of a short circuit in the wiring. Also the output of the alternator to the starter is protected by tow fusible links that looks like large caliber wires melting at instances of overload. Replacement of a fusible link requires that negative battery cable should be removed, burned out link should be removed and be replaced with a new one while ensuring the cause of overload is found before fixing the link.