My Garage
My Account
Cart
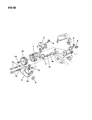
Genuine Dodge Ramcharger Air Injection Pump
SAI Pump- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
1 Air Injection Pump found
Dodge Ramcharger Air Injection Pump
In Dodge Ramcharger vehicles, the Secondary Air Injection Pump is quite important as it is incorporated in the Air Injection Reactor or better still, AIR system, which has the main mission of injecting fresh air into the exhaust system of the vehicle so as to help in the oxidation of unburned fuel and thus help to minimize on: The HC and CO emissions. Also in Dodge Ramcharger models, the air pump uses air pressure during start-up to expel air into the exhaust ports to cut down on emissions from an over-rich air to fuel mixture. Once the engine reaches normal temperatures the system then supplies air to the catalytic converter for a second stage emission control. The design elements include diverter valves and one way check valves which ensure that the pump is not struck by back fires and is well protected from exhaust gases. In general, the Secondary Air Injection Pump is vital to preserving emission control and maximizing fuel economy in the Dodge Ramcharger automobiles.
Looking for affordable and high-quality auto parts? Then you have already arrived at the proper online shop. We offer all Dodge Ramcharger Air Injection Pump at great affordable prices. Moreover, all genuine Dodge Ramcharger Air Injection Pump come with a manufacturer's warranty. In the long run, you would realize you have saved a lot of trouble and money with OEM parts from here.
Dodge Ramcharger Air Injection Pump Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What are the procedures for maintaining and troubleshooting an air injection system and Air Injection Pump on Dodge Ramcharger?A:This air injection system has the responsibility of maintaining low carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon; this sub-system has an air supply pipe, an air control valve, a check valve injection tubes and connecting hoses. It works by blowing in fresh air into the hot exhaust stream, thus achieving more combustion of the remaining mixed gases, thus minimizing emission and making some of them to evaporate into carbon dioxide and water. At other operating modes, e.g. higher engine speed, the air control valve dumps air to the atmosphere to prevent overheating of the exhaust system. There are three types of air control valves: a relief valve that controls the amount of output of the pump; a diverter valve that ensures that back firing does not occur during occasions like rapid deceleration; and the switch/relief valve that directs the flow of the air injection depending on engine heat . To do this, stop the engine and with the air supply hose disconnected, one should be able to feel air flow at the pump outlet. In the event that the pump is damaged, it should be replaced that is if there is enough budget. Concerning the relief and diverter valves, if the noise is loud or is air, then there is a problem and the valves must be replaced. Grossly, the switch/relief valve should not release air at idle; if it does, then the valve must be changed. The check valve is checked by examining its inlet tube, for exhaust gas; if experienced, the check valve needs replacement. Some specifications need to be met as follows; when removing fittings, mark the hoses for reconnection, replace any damaged parts, and be certain that all gaskets are new and the hoses are in good condition. For the air supply pump, slacken the drivebelt, replace the ruined unit with the undergoing label wires and hoses and tighten the new pumps' drivebelt to the correct tension.