My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Dodge Challenger Catalytic Converter
Cat. Converter- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
60 Catalytic Converters found
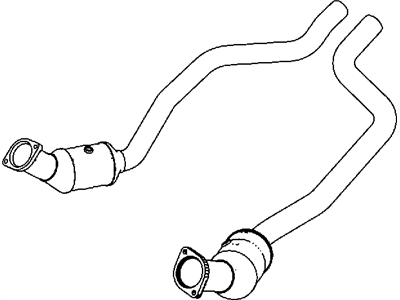
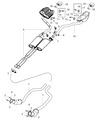
Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 68038393AI$1242.20 MSRP: $1820.00You Save: $577.80 (32%)Dodge Challenger Converter-Front
Part Number: 5039056AG$3288.50 MSRP: $4995.00You Save: $1706.50 (35%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 5039056AB$3288.50 MSRP: $4995.00You Save: $1706.50 (35%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 5039056AF$3288.50 MSRP: $4995.00You Save: $1706.50 (35%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 5039056AE$3288.50 MSRP: $4995.00You Save: $1706.50 (35%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 5039055AF$3118.00 MSRP: $4710.00You Save: $1592.00 (34%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 5039055AE$3118.00 MSRP: $4710.00You Save: $1592.00 (34%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 5039055AD$3118.00 MSRP: $4710.00You Save: $1592.00 (34%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 5039055AB$3118.00 MSRP: $4710.00You Save: $1592.00 (34%)Dodge Challenger Exhaust Converter
Part Number: 68474162AD$2790.30 MSRP: $4100.00You Save: $1309.70 (32%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 68038392AC$1824.15 MSRP: $2675.00You Save: $850.85 (32%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 68038390AE$1869.35 MSRP: $2760.00You Save: $890.65 (33%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 68038391AB$1976.05 MSRP: $2910.00You Save: $933.95 (33%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
Part Number: 68038393AD$1242.20 MSRP: $1820.00You Save: $577.80 (32%)Dodge Challenger Front Catalytic Converter And Pipe
Part Number: 68276680AA$1399.75 MSRP: $2080.00You Save: $680.25 (33%)Dodge Challenger Converter-Front
Part Number: 68038390AB$1869.35 MSRP: $2760.00You Save: $890.65 (33%)Dodge Challenger Front Converter
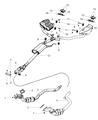
Part Number: 68057163AF$2857.45 MSRP: $4210.00You Save: $1352.55 (33%)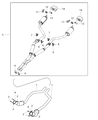
Dodge Challenger Front Catalytic Converter And Pipe
Part Number: 68281725AA$672.84 MSRP: $972.00You Save: $299.16 (31%)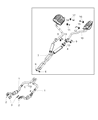
Dodge Challenger Front Catalytic Converter And Pipe
Part Number: 68276676AA$429.42 MSRP: $622.00You Save: $192.58 (31%)
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 60 Results
Dodge Challenger Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an important part of the emissions control system in the Dodge Challenger, it utilizes a chemical reaction to transform toxic gasses into less pollutant gasses. Usually, these converters are intended to last throughout the lifetime of the vehicle but they can fail prematurely especially due to fuel mixtures. They cannot be refurbished and as such, they must be replaced whenever they are worn out. As for the years the Dodge Challenger has incorporated a number of styles of the catalytic converters. Originally it had ceramic beads, while the latest ones use honeycomb model, increasing the productivity of gases circulation and contact with the catalyst. Utilizing stainless steel as well as aluminum the catalytic converter is designed to be quite robust and long-lasting, which makes it quite an important part of the exhaust system in the new Dodge Challenger.
Looking for affordable and high-quality auto parts? Then you have already arrived at the proper online shop. We offer all Dodge Challenger Catalytic Converter at great affordable prices. Moreover, all genuine Dodge Challenger Catalytic Converter come with a manufacturer's warranty. In the long run, you would realize you have saved a lot of trouble and money with OEM parts from here.
Dodge Challenger Catalytic Converter Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What is a catalytic converter and how does it function in the exhaust system on Dodge Challenger?A:A catalytic converter is an emission control device in the exhaust system that reduces pollutants in the exhaust gas stream, with two types, an oxidation catalyst to lower the emissions of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide, and a reduction catalyst to minimise the emission of oxides of nitrogen. All the models are fitted with two Three-Way Catalysts situated one below the other exhaust manifold flange with inlet pipe and mounting flange and an outlet pipe held by clamps. There is like a possibility of a particular product having a mechanical failure, therefore should it be suspected, it is wise to take it for diagnosis to a dealer or an authorized workshop. Leak check and structural damage or corrosion must be a routine check, and if any of these are seen, then the converter must be changed. To check for a restricted converter, it is always possible to use a vacuum gauge in order to measure the intake vacuum at idle and during a test throttle opening; if there will be a substantial drop in the middle of the readings, it is likely that a converter is restricted. For replacement, it should be secured on a repair rack and penetrating oil put on the bolts and nuts before removing the Oxygen Sensor and other necessary bolts and clamps. The catalytic converter can then be taken out and when reinstalling a new flange gasket should be used In addition, new bolts and nuts should be used every time with anti-seize compound for easy removal in future. When reconnected a converter, the support bracket has to be put in position using new fasteners that have to be tightened with force.
Related Dodge Challenger Parts
Browse by Year
2023 Catalytic Converter 2022 Catalytic Converter 2021 Catalytic Converter 2020 Catalytic Converter 2019 Catalytic Converter 2018 Catalytic Converter 2017 Catalytic Converter 2016 Catalytic Converter 2015 Catalytic Converter 2014 Catalytic Converter 2013 Catalytic Converter 2012 Catalytic Converter 2011 Catalytic Converter 2010 Catalytic Converter 2009 Catalytic Converter 2008 Catalytic Converter