My Garage
My Account
Cart
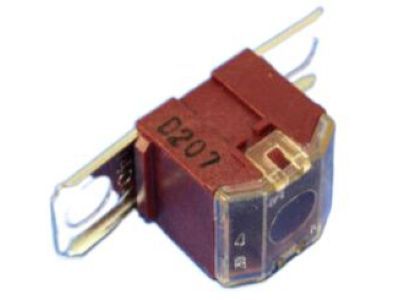
Genuine Dodge Neon Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
17 Fuses found
Dodge Neon Fuse
Looking for affordable and high-quality auto parts? Then you have already arrived at the proper online shop. We offer all Dodge Neon Fuse at great affordable prices. Moreover, all genuine Dodge Neon Fuse come with a manufacturer's warranty. In the long run, you would realize you have saved a lot of trouble and money with OEM parts from here.
Dodge Neon Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
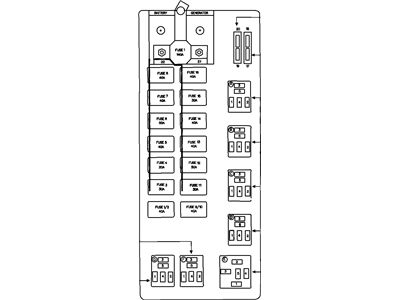
- Q: What are the methods and precautions for checking and replacing fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links in electrical systems on Dodge Neon?A:The electrical circuits of the vehicle are protected by fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links, of which the fuse blocks are located at the left of the instrument panel and in the engine compartment. They are individualized to a circuit, and the circuits are labeled on the cover of the fuse panel. Miniature fuses with blade terminal are utilized; the fuses have a very small and can be easily replaced; if an electrical part has a problem then looking at the fuse should be done. A test light can be used to inspect power on the exposed terminal tips of each fuse by touching each terminal of the fuse as this will make a fuse go 'blown' if power is present at one terminal of the fuse but not the other; the element between the terminals of a 'blown' fuse will have melted. Blown fuses should be replaced with the correct type cross they can be physically swapped with other fuses despite the same size and shape although this is not advised due to the protection required by each circuit. If a replacement fuse is weakened and it goes off as soon as it is replaced, then the actual problem-most often, a short circuit due to a damaged or worn wire-should be fixed before attempting the replacement again. Other circuits are protected by fusible links, which can be used in a circuit that is not usually fused or in circuits with high current, with the cartridge type fusible links located in the engine compartment fusible link box and similar to a large fuse; these can be replaced by unplugging and inserting the link of the same amperage with the negative battery cable or remote ground terminal disconnected.