My Garage
My Account
Cart
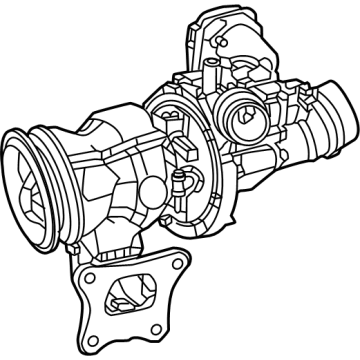
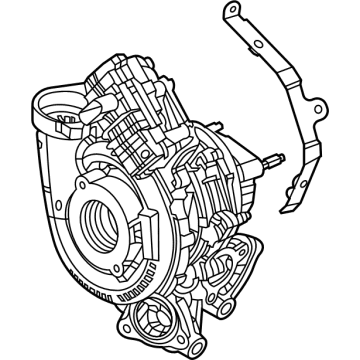
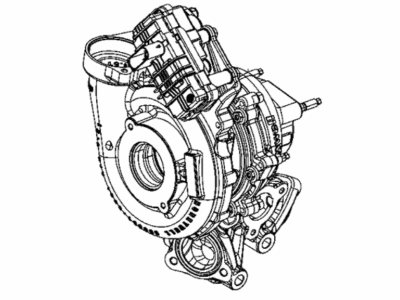
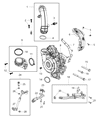
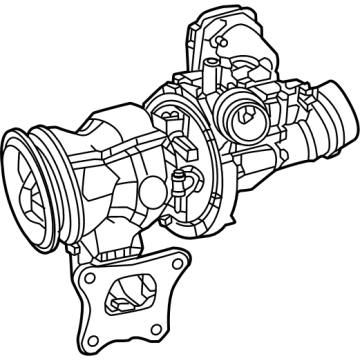
Genuine Ram 1500 Turbocharger
Turbo- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
9 Turbochargers found
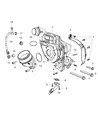
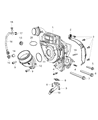
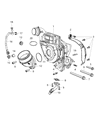
Ram 1500 Turbocharger
Part Number: 68211213AD$1548.60 MSRP: $2395.00You Save: $846.40 (36%)FREE Shipping
Ram 1500 Turbocharger
A compressor commonly known as the ram air in Ram 1500 vehicles is an important feature of the vehicle that boosts the engine power that pushes air under compression to the combustion chamber thus increasing the general performance of the vehicle. Unlike other superchargers, Ram 1500 Turbochargers are exhaust driven and uses the energy from exhaust gases to produce boost air pressure for enhancing the engine. Of course, they suffer from lag resulting from pressure build-up, but new trends such as twin-scroll and variable geometry turbos, as well as electrical boost assist (E-turbo) to increase turbos' response. Turbocharging is typical for both petrol and diesel engines, and main producers of turbochargers are currently operating under such brands as Garrett Motion and BorgWarner. As much as turbocharger helps in fuel economy and better performing engines it has its demerits main of which are high exhaust temperatures and can be unsafe.
Looking for affordable and high-quality auto parts? Then you have already arrived at the proper online shop. We offer all Ram 1500 Turbocharger at great affordable prices. Moreover, all genuine Ram 1500 Turbocharger come with a manufacturer's warranty. In the long run, you would realize you have saved a lot of trouble and money with OEM parts from here.
Ram 1500 Turbocharger Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to Replace a Turbocharger on a Ram 1500?A:Disconnect the negative battery cables and drain coolant. Remove air filter housing, hoses, tubes, wiring, and oil supply line. Remove coolant lines and engine-driven fan/shroud (2012+). Raise vehicle and support on jackstands. Remove right inner fender and engine mount. Remove exhaust bracket and V-band clamp. Lower vehicle and remove Grid Heater relay. Remove turbocharger mounting nuts and turbocharger. Clean turbocharger and exhaust manifold. Bolt turbocharger onto exhaust manifold with new gasket. Reinstall oil drain line and coolant lines. Prime center bearing with oil and install supply line. Reverse of removal for remainder of installation. Tighten turbocharger-to-exhaust manifold nuts.
- Q: What Are the Inspections That Can Be Done by the Owner on a Turbocharger on Ram 1500?A:A turbocharger improves engine power, reduces exhaust smoke density, enhances fuel economy, decreases engine noise, and mitigates the effects of lower-density air at higher altitudes and it achieves this by using an exhaust gas-driven turbine to pressurize the air entering the combustion chambers. Turbocharged models have an Intercooler that lowers the temperature of the compressed air intake charge, resulting in increased combustion efficiency, power, and reduced emissions. It is crucial to check for leaks in the oil supply line and tighten any fittings if necessary. If the supply line itself is leaking, it should be replaced. The oil return line should also be inspected for obstructions, as a blocked return line can cause oil loss through the turbocharger seals. Burned oil on the turbine housing is a sign of a blocked return line.